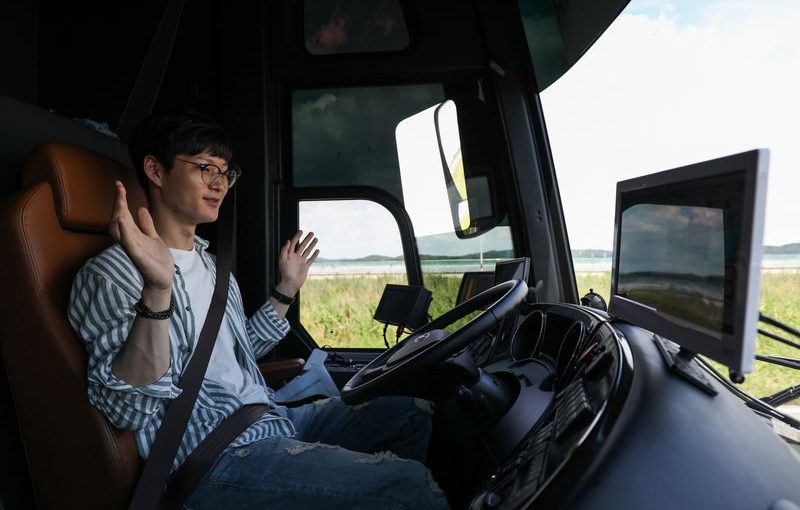
THE FUTURE IS HERE: A driver rides inside an autonomous 5G connected bus, operated by KT Corp., in Hwaseong, South Korea. (Photo: SeongJoon Cho/Bloomberg)
By Yuko Takeo
A war is raging between the various 5G players to get the biggest share of the pie. Even Jio is rattled and has gone back on its promise of not charging for calls. It remains to be seen who wins the 5G battle and ushers in the future…
Self-driving cars, remote robotic surgery, autonomous weapons — all that and much more is set to be delivered via the 5G wireless network, which promises to transform our lives and add trillions of dollars to the global economy every year.
New products, services, business models and entire industries will be born as 5G provides a huge leap forward in speed, capacity and connectivity.
Now economists are putting a number on the coming transformation, with IHS Markit estimating 5G will drive an extra $12 trillion of annual sales in 2035. That’s about the size of China’s economy last year.
For consumers, the first changes will be faster mobile data speeds — eventually up to 100 times quicker than those of 4G, letting people download full-length movies in seconds. At work, the trend will be greater automation of tasks and digital connectivity, driving a new wave of productivity gains for some industries.
While the rollout of 5G is already underway in South Korea and select U.S. cities, the most dramatic changes are still some years away. Many will come with risks and painful disruptions.
Here are some ways 5G will change the world.
Internet of Things
The internet of things refers to all the machines and devices linked through the internet, and its enormous growth is likely imminent as 5G comes online. There are expected to be 125 billion devices linked by 2030, up from 11 billion last year, according analysts at DBS Group Research.
This leap forward in connectivity will be key to the spread of artificial intelligence and machine learning, enabling massive amounts of data to be collected from remote and mobile sensors and analyzed in real time. This will drive everything from home appliances that order groceries to autonomous vehicles to smart cities. China’s ambition to dominate these industries of the future including the 5G technology itself, as outlined in the Made in China 2025 blueprint, has contributed to trade tensions with the U.S.
Transport & Logistics
The future of transport starts with driverless cars, and in the early days of 5G the automotive sector is likely to see some of the biggest changes. Everyone from Apple Inc. to Uber Technologies Inc. is looking to build self-driving cars. But while test cars are already on the roads in some cities, the commercial introduction of these vehicles — essentially large, mobile computers processing enormous amounts of data in real time — won’t be possible without the speed and capacity of fully deployed 5G networks.
5G and autonomous vehicles also promise to revolutionize shipping and logistics. That could mean platoons of linked autonomous trucks and “ghost” cargo ships, as well as dramatic improvements in logistic efficiency. Millions of truck, tractor, bus and taxi drivers around the world could lose their jobs, though of course new ones would be created elsewhere. In testing, the Port of Hamburg has begun installing sensors on ships to track movement and environmental data in real time, enabling employees equipped with smart glasses to visualize the action, via augmented reality, improving traffic flow and efficiency.

Health Care
Feeling unwell? One day you could order a house call from a self-driving mini-clinic that offers automated diagnostic tests and video-links to a range of doctors. That’s one vision of the future of health care, in which rapid advances in data transmission, robotics and AI change the quality of care and the way it is delivered. That could also include remote robotics-assisted operations, and even partially automated surgeries. Elderly people, particularly those in rural or otherwise under-served communities, should benefit, particularly in places like Japan where the countryside is being depopulated.
5G will also advance more personalized, data-driven medicine, partly via wearable technologies that will be able to monitor not only your physical condition but emotional and mental states as well — and all in real time. In Singapore, for example, cognitive and behavioral science startup Cognifyx has recently teamed up with ride-hailing service Grab to test drivers for mental fatigue.
In the Office
Office work will get a lot smarter. Advances in AI and machine learning made possible by 5G networks will mean fewer white collar workers will be engaged in repetitive tasks, even cognitive ones such as accounting and data processing. In most cases, smart machines won’t take over entire jobs but will instead perform tasks that are key parts of jobs. Workers who can collaborate with intelligent machines and who have higher-order cognitive skills such as problem-solving and critical thinking will be most in demand.
In the Factory
The factory of the future will also rely on 5G to enable augmented reality, autonomous mobility, sensor networks and machine learning. The result will be “extreme automation” and dramatic advances in productivity. Japanese machine tool maker Yamazaki Mazak recently helped launch the UK’s first 5G factory trials, using sensors for real-time monitoring and data collection, helping to speed up and better maintain automation systems.
Security and War
5G has implications for public and national security. To begin with, the extreme interconnectedness itself poses risks, making everything from individual households to energy grids more vulnerable to hackers. The 5G network will also power the development of fully autonomous weapons that make their own decisions to fire on targets, as well as the unprecedented tracking of people in public in real time using facial recognition technology.
Given the power of 5G technology, it is no surprise that it has also become a proxy for the broader power struggles between the U.S. and China. Huawei Technologies Co. has been targeted by the U.S. government and its Western allies as it pushes for a leadership role in rolling out the 5G network, given its close ties to Beijing.
Adding Up
IHS Markit views 5G as on par with the printing press, electricity and the steam engine — a technology that from 2020 to 2035 will add real gross domestic product equivalent to an economy the size of India’s.
“The profound effects arising from these innovations range widely — from the positive impacts for human and machine productivity to ultimately elevating the living standards for people around the world,” IHS Markit analysts wrote.
Courtesy: Bloomberg
UNDERSTANDING 5G
«…I should be already at home, but a last-minute e-mail made me lose track of time. It´s colder than yesterday, so while I wait for the elevator to arrive I turn the living room´s heating through my cell phone; I´m pretty sure that my wife will arrive home sooner than me and she will appreciate it…Just when I start my car´s engine I receive a call from her, she forgot her smartphone at the office again and she needs me to open the garage door through mine. She says “thank you, honey” as the noise of the gate elevating is heard in the background. As soon as I get home, I´m welcomed by a couple of gardener drones which help my wife to take care of her plants. They´re infallible when it comes to keep track of humidity and heat required by each one of them. Wow! It seems like they read my mind, as their daily report is just been delivered to my smartphone notifying me about the lack of fertilizer. I confirm the order placed automatically by the system, and I step inside the house…»
For this story about any given day after work to become something quotidian without any bandwidth collapse, we are still missing a development of a new wireless network capable of making it completely plausible: 5G technology, in other words, the fifth generation of mobile communications. Let´s dive into it.
5G facts are mind-boggling
5G is the fifth generation of mobile connectivity. A little over 3 years ago, LTE or what we know as 4G connectivity arrived to shake the smartphone world and boost data transmission speed, so we are not unfamiliar to this concept anymore. However, it seems that what we experienced at that time will pale in comparison to the vast array of possibilities carried under its belt by this new generation of wireless connectivity, which is being built over the foundations of the previous one.
The best way to illustrate this is by sheer data. The average 4G LTE transmission speed currently available for our smartphones in Spain, for instance, is somewhere around the 21 Mbps mark, allowing us uncut music streaming and prompt web surfing. Well then, 5G connection speed will manage to achieve over 10 Gbps, that is to say, between 100 and 1000 times faster, making it possible to download, for example, a HD movie in 10 seconds.
This remarkable speed is joined by a huge capability for data transmission, 10 Tbps, and a density of 1 million nodes per Km². Besides, it is expected that connection latency shrinks from 50 miliseconds to just 1 milisecond. In other words, 5G technology will allow a delay time reduction in communications, an increase in information transfer rate, a significant improvement in mobile coverage and will allow millions of devices to be connected simultaneously. This is, in fact, one of the key factors in foreseeing that 5G technology will go far beyond the realm of smartphones.
Is 5G technology the missing piece in the puzzle of Smart Cities?
Thanks to these data regarding the improvement in transmission speed and connection quality, 5G network plunges us into the age of “everything connected” or the Internet of Things. It will allow us to create a true ecosystem capable of transcending the smartphone world, possibly becoming the missing piece of the puzzle to build true smart cities.
5G technology will be a key factor to allow millions of devices to be connected simultaneously in highly populated areas. In addition, it will enable communication between those devices, linking a smartphone to the garage door at home or the alarm clock to the coffee maker, so that we can wake up and find freshly brewed coffee. But there´s so much more to it. With 5G technology Car2Car connections could be increasingly efficient and safe, consequently allowing real time feed about traffic conditions or accidents. Same could happen with 360° virtual reality, which would likely take advantage of latency decrease and information transfer capability to generate true virtual environments.
Speaking of latency, data-based voice calls or video calls, like Skype, will be the ones to benefit the most, since they won´t experience any delay time or failure. Same will apply to mobile connectivity: with 5G technology we will be able to stream a movie while travelling by train with the same quality as if we were watching it at home.
The medical field won´t stay out of the innovations promised by this new standard, as it is already being discussed how 5G networks could make wireless health care or even remote surgical procedures a reality.
How long will it take to 5G technology to arrive?
All researches available point to 2020 as the year when 5G technology will be consolidated, although the network will begin to be implemented in 2018 and the majority of operators, regulatory bodies and manufacturers are currently engaged in talks to arrange a standard, as it happened before the deploy of 4G technology. In fact, Qualcomm has already developed the first 5G modem, specifically created to support this type of network, thus paving the way for the new generation of smartphones. On its part, the European Union seeks complete 5G coverage by 2025. At these rapid rate of evolution, that date is already around the corner.
Courtesy: I’mnovation #hub
