Goa is abuzz with excitement as vintage bike and car owners, users, collectors and fans are decking […]

STAY HOOKED ON TO HEALTH, THE NUTRITIONAL CATCH OF FISH
Jan 18- Jan 24 2025, MIND & BODY, HEART & SOUL January 17, 2025A Q&A interview with Dr Amit Dias on the goodness of eating fish in our diet
While Goa celebrated the Aqua Goa: Mega Fish Festival last week, we caught up with Dr Amit Dias to dive deeper into the nutritional benefits of fish in our diet. He simplified and unpacked the seafood secrets and said “It’s good to have fish in your diet.” Here’s more information to promote the consumption of more fish in your diet.
Goan Observer: Doctor, in view of the Aqua Goa Seafood Festival held in Panjim recently , we would like to learn about the role of fish for our health. Could you start by helping us understand the nutritive value of fish?
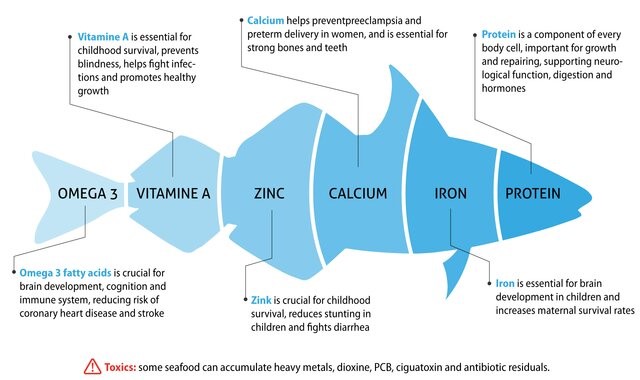
Dr Amit Dias: Fish is an excellent source of high-quality protein, essential vitamins and minerals. It is rich in omega-3 fatty acids which are beneficial for heart and brain health. Fish also provides significant amounts of vitamins D and B12, selenium, iodine and zinc. Oily fish like mackerel, sardines and salmon are particularly nutrient-dense, offering high amounts of omega-3s and fat-soluble vitamins.
Q: A lot is mentioned about omega fatty acids- what are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, and why are they important?
A: Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats that our body cannot produce.
Omega-3s (found in fatty fish) are critical for heart, brain, and eye health, as well as reducing inflammation.
Omega-6s (found in vegetable oils and nuts) are important for growth and brain function. However, a balance between omega-3 and omega-6 is crucial to prevent chronic inflammation.
Q: Great, how how much fish should one eat in a week?
A: That would depend on the region you live. The American Heart Association recommends eating fish at least twice a week, with each serving being about 3.5 ounces cooked or ¾ cup of flaked fish. Incorporating a variety of fatty and lean fish ensures maximum health benefits.
Q: What are the common fishes consumed by the people in Goa, and what are their nutritive benefits?
A: Goa is blessed with a wide variety of fish, each offering unique nutritional benefits:
• Mackerel (bangda): High in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and selenium.
• Kingfish (viswon): Rich in protein, vitamin D, and low in fat.
• Pomfret (pomplet): Contains good-quality protein and moderate amounts of omega-3s.
• Sardines (talle): Extremely rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B12, and calcium (especially when consumed with bones).
• Giant Sea Perch (chonak): Rich in protein, vitamins B12 and D, and omega-3s.
• Indian Dog Shark (mori): A good source of lean protein and vitamins, with a low-fat content.
• Red Snapper (tambso): High in lean protein and contains moderate omega-3 levels.
• Dhema (dodyaro): Known for its high protein and low-fat content.
• Bombay Duck (bombil): Rich in protein and low in fat, with a soft texture.
• Lady Fish (mudoshi): Provides high-quality protein, low fat, and is rich in vitamin B12, phosphorus, and selenium. Ideal for muscle repair and boosting immunity.
• Lemon Fish (modso): A rich source of lean protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential vitamins such as B6 and B12. It is low in fat and supports brain and heart health.
Including these in your diet can help meet nutritional needs and provide variety.
Q: Which diseases that are known to be prevented by eating fish?
A: Research has shown that eating fish regularly can help prevent several diseases and health conditions due to its rich nutritional profile, particularly its high content of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. Here are some diseases that can be prevented or mitigated by consuming fish:
Cardiovascular Diseases (Heart Disease, Stroke): Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) in fish reduce triglyceride levels, improve blood vessel function, lower blood pressure, and decrease the risk of arrhythmias. Regular fish consumption is associated with reduced risks of heart attack and stroke.
Cognitive Decline and Alzheimer’s Disease: Omega-3s support brain health, improve cognitive function, and reduce inflammation in the brain. Fish is a good source of vitamin D and antioxidants, which may help delay the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
Depression and Mental Health Disorders: Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that enhances mood and reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety. Studies show that fish consumption is associated with a lower prevalence of depression and bipolar disorder.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): The DHA in fish supports retinal health and reduces the risk of vision loss caused by AMD, a leading cause of blindness in older adults.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Fish has anti-inflammatory properties due to its omega-3 content, which helps reduce joint inflammation and pain in arthritis patients.
Type 2 Diabetes: Fish helps improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation, which are important in managing and preventing diabetes. Its high protein content helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
Asthma in Children: Omega-3 fatty acids reduce airway inflammation and may lower the risk of developing asthma, particularly in children.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS): Pregnant women who consume fish rich in omega-3s can help support proper neural and visual development in their babies, reducing the risk of SIDS.
Osteoporosis: Fish provides vitamin D and calcium, essential for maintaining bone density and preventing bone loss.
Cancer Prevention: Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids may have protective effects against certain cancers, such as breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer, by reducing inflammation and inhibiting tumor growth.
Skin and Hair benefits: Fish consumption can improve skin and hair health by providing essential fatty acids that enhance skin elasticity and hydration and promote hair growth.
One should be clear that fish is only a source of nutrition and this can also be availed from other sources. It does not mean that people who do not consume fish with get the health problems I mentioned earlier.
Q: How does the preparation of fish affect its nutritive value?
Dr. Dias: The method of preparation greatly impacts the nutritional content of fish:
• Grilling, baking, or steaming: This preserves most nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins.
• Deep or shallow frying: This adds calories and may degrade omega-3 fatty acids due to high heat. In Goa we have a lot of deep and shallow fried fish.
• Smoking or curing can increase sodium levels, which may not be ideal for people with hypertension.
Choosing healthier cooking methods can ensure you get the most benefits from fish. Fish Curry and rice is the staple meals consumed in Goa.
Q: What is the nutritive value of crabs?
Dr. Dias: Crabs are low in fat but packed with high-quality protein, selenium, zinc, and vitamin B12. They also contain omega-3 fatty acids, which support brain and heart health, though not as much as oily fish. Crab meat is particularly beneficial for maintaining muscle and supporting immune function.
Q: What about shellfish?
Dr. Dias: Shellfish such as shrimp, mussels, and clams are nutrient-rich, offering protein, iodine, iron, zinc, and vitamin B12. They are also low in calories and high in omega-3s. However, some people may need to monitor their intake due to the cholesterol content in shellfish. It can transmit disease if not adequately cooked.
Q: Can I get the same benefits by taking omega-3 oral supplements instead of fish?
Dr. Dias: Omega-3 supplements like fish oil can be beneficial, especially for those who cannot consume fish. However, whole fish also provides additional nutrients like protein, vitamins, and minerals, which supplements lack. Combining fish consumption with supplements (if needed) is a balanced approach.
Q: What is cod liver oil ? and what is its importance in health?
Dr. Dias: Cod liver oil, extracted from codfish liver, is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin A, and vitamin D. It supports bone health, boosts immunity, and reduces inflammation. However, it must be taken in recommended amounts to avoid harmful effects.
Q: What about mercury in fish? how can we avoid it?
Dr. Dias: Mercury contamination is a concern in larger predatory fish like shark, swordfish, and tuna. Mercury can affect neurological development, particularly in pregnant women and young children.
• Choose smaller fish like sardines or mackerel, which have lower mercury levels.
• Limit consumption of high-mercury fish.
• Diversify seafood choices to minimize exposure.
Q: What about formalin added to fish? What are the health hazards, and how can we prevent it?
Dr. Dias: Formalin, a preservative containing formaldehyde, is sometimes illegally added to fish to extend freshness. Consuming such fish can cause gastrointestinal distress, respiratory issues, and is linked to carcinogenic effects with long-term exposure. It was in the news a few years ago.
To prevent this:
Buy fish from trusted vendors.
Check for a strong chemical smell or unusually firm texture in fish.
Rinse fish thoroughly and cook it properly to reduce potential residue.
Q: What are the diseases that can be transmitted through seafood?
Dr. Dias: One can get food poisoning if the sea food is not cooked adequately. Muscles are sometimes consumed raw and can cause gastro enteritis. Other diseases transmitted through seafood include:
• Fish tapeworm (Diphyllobothriasis): Caused by consuming raw or undercooked freshwater fish.
• Vibrio infections: From raw or undercooked shellfish – Cholera.
• Parasitic infections (e.g., anisakiasis): From raw fish or squid containing the worm
• Hepatitis A & E: From contaminated shellfish.
Proper cooking and handling can prevent these infections.
Q: Is there evidence that people with a predominantly fish-based diet are healthier?
Dr. Dias: Yes, research shows that populations with fish-based diets, such as the Mediterranean and Okinawan diets, have lower rates of cardiovascular diseases, better cognitive health, and increased longevity. Fish provides essential nutrients that promote overall well-being.
Q: What is your message to the readers?
Dr. Dias: Fish is a superfood packed with essential nutrients. Its nice ot have a Fish in your dish. Choose fresh, locally available fish, prepare it healthily, and enjoy it responsibly while being mindful of mercury and additives like formalin. A balanced diet that includes fish can significantly improve your overall health and well-being.
















